🇮🇳 India’s Chip-Based Biometric E-Passports: A Leap into Secure and Efficient Travel
Explore how India’s chip-based biometric e-passports enhance security, improve global mobility, and streamline the travel experience for Indian citizens.
✈️ Introduction: A Passport to the Future
In a world rapidly evolving through digital innovation, India has taken a giant leap forward in transforming international travel. The rollout of chip-based biometric e-passports introduces a secure, tamper-proof, and internationally accepted upgrade to the traditional passport system. With built-in chips storing biometric data, this high-tech travel document enhances both traveler security and immigration efficiency.
Whether you’re a frequent flyer or a first-time traveler, understanding the nuances of this next-gen passport is essential. This guide dives deep into how chip-based biometric e-passports work, their benefits, how they compare with traditional passports, and general information about Indian passports, including eligibility, ranking, and application process.
🛂 General Overview: Indian Passports at a Glance
📘 What Is an Indian Passport?
An Indian passport is an official travel document issued by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) to Indian citizens for international travel and identity verification. It confirms the passport holder’s identity and nationality.
🧾 Types of Indian Passports
- Ordinary Passport (Blue Cover):
- Issued to regular Indian citizens.
- Used for personal or business travel.
- Valid for 10 years (renewable).
- Diplomatic Passport (Maroon Cover):
- Issued to diplomats and top government officials.
- Official Passport (White Cover):
- Issued to individuals representing the Indian government on official duties.
✅ Eligibility for an Indian Passport
To be eligible for an Indian passport, an individual must:
- Be an Indian citizen as per the Indian Citizenship Act, 1955.
- Provide valid documents proving identity, address, and date of birth.
- Have no pending criminal cases or restraining legal conditions.
🌍 Indian Passport Ranking (2025)
As per the Henley Passport Index, the Indian passport ranks 83rd in 2025. It allows visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to around 62 countries, including nations like:
- Indonesia
- Bhutan
- Maldives
- Sri Lanka (e-visa)
- Nepal (without a passport)
✨ Tip: Chip-based biometric passports are expected to improve India’s passport strength in the coming years by meeting global security benchmarks.
🆕 What Are Chip-Based Biometric E-Passports?
Chip-based biometric e-passports are enhanced versions of regular passports, equipped with:
- An embedded RFID chip.
- Digitally stored biometric information, including the passport holder’s photograph, fingerprints, and personal details.
- High-level encryption to prevent unauthorized access or duplication.
These passports follow the ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization) standards, ensuring global interoperability.
🔐 Key Features of India’s E-Passports
| Feature | Traditional Passport | Biometric E-Passport |
|---|---|---|
| RFID Chip | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Biometric Authentication | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| ICAO Compliance | ❌ Partial | ✅ Full |
| Tamper Detection | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Machine-Readable Zone (MRZ) | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Contactless Chip Communication | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
📡 Technical Features
- Passive Authentication (PA): Verifies digital signature on data.
- Active Authentication (AA): Ensures the chip hasn’t been cloned.
- Extended Access Control (EAC): Restricts access to sensitive biometric data.
- Basic Access Control (BAC): Requires authentication before reading the chip.
These features significantly reduce the risk of:
- Passport duplication.
- Data theft.
- Identity fraud at borders.
🏁 Rollout of E-Passports in India
The pilot launch began in 2022, and full-scale production was initiated in 2024 as part of Passport Seva Programme 2.0. The initial phase covered 13 major cities:
- Delhi
- Chennai
- Hyderabad
- Jaipur
- Nagpur
- Goa
- Jammu
- Bhubaneswar
- Shimla
- Ranchi
- Raipur
- Amritsar
- Surat
The India Security Press (ISP) in Nashik is now fully equipped to manufacture e-passports for wider rollout in 2025.
📑 Application Process for Indian E-Passports
The process is identical to regular passport applications and involves:
- Online Registration:
- Visit the Passport Seva Portal.
- Create an account and complete the e-form.
- Document Submission:
- Proof of identity (Aadhaar, PAN, voter ID)
- Proof of address
- Birth certificate (for minors)
- Appointment Booking:
- Schedule a visit at your nearest Passport Seva Kendra (PSK).
- Biometric Capture & Police Verification:
- Fingerprints and photograph are taken.
- Police verification is mandatory for first-time applicants.
- Issuance & Delivery:
- Passports are printed and dispatched via India Post.
- For e-passports, RFID chip encoding is included in the final print.
💡 Benefits of Chip-Based Biometric E-Passports
⏱ Faster Immigration Clearance
E-passport holders benefit from automated gates at international airports, reducing wait times.
🔐 Enhanced Security
The encrypted chip makes it nearly impossible to forge or duplicate the passport.
🌐 Global Recognition
Full ICAO compliance means global trust and interoperability, opening more visa-free opportunities.
📈 Economic & Technological Advancement
Boosts India’s image as a tech-forward nation and supports Digital India and Make in India initiatives.
❓ Addressing Concerns
⚠️ Data Privacy
Concern: What if my biometric data is misused?
Reassurance: The MEA confirms that all data is stored in a digitally signed and encrypted format. Only authorized systems at immigration checkpoints can access this data.
📉 Cost and Accessibility
Currently, the price remains the same as regular passports (₹1,500 for 10-year validity). As mass production scales up, no additional charges are expected for e-passports.
🌏 India Among Global Leaders in E-Passport Adoption
India joins countries like:
- Germany
- USA
- Australia
- Japan
- UK
These nations have already adopted e-passports to enhance national security and streamline traveler experience.
🔍 Infographic: Traditional vs. Chip-Based E-Passport
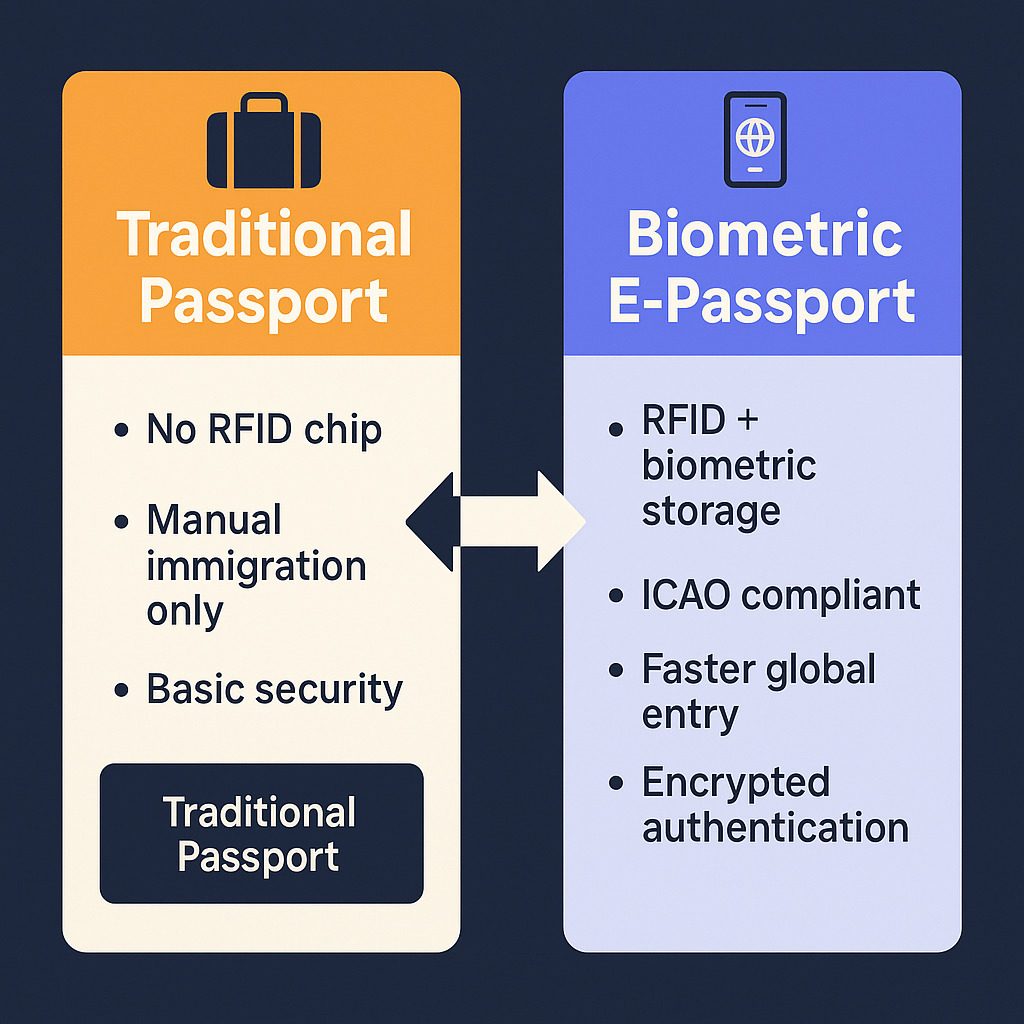
🗓 Validity & Renewal
- Standard validity: 10 years
- For minors under 18: 5 years
- Renewal process: Similar to application (can be initiated 1 year before expiry)
🧭 Internal Linking for Deeper Insight
For travelers considering other passport or visa services, explore our recent blogs:
- 👉 Top 5 International travel destination to explore in monsoon 2025
- 👉 Visa-Free Countries for Indian Passport Holders in 2025
📢 Conclusion: A Passport Ready for Tomorrow
The launch of chip-based biometric e-passports is more than just a technological upgrade—it’s a commitment to safer, faster, and globally accepted travel for Indian citizens. As India accelerates into a digital future, e-passports will be a crucial enabler for smoother global mobility and elevated trust in international corridors.
🗣 Call to Action
Are you planning to apply for your e-passport soon?
🧳 Share your thoughts or experiences in the comments below!
💬 Got questions? Let us know—we’d love to help.
🔗 Don’t forget to explore more travel updates at travellerscheckin
.


0 Comment